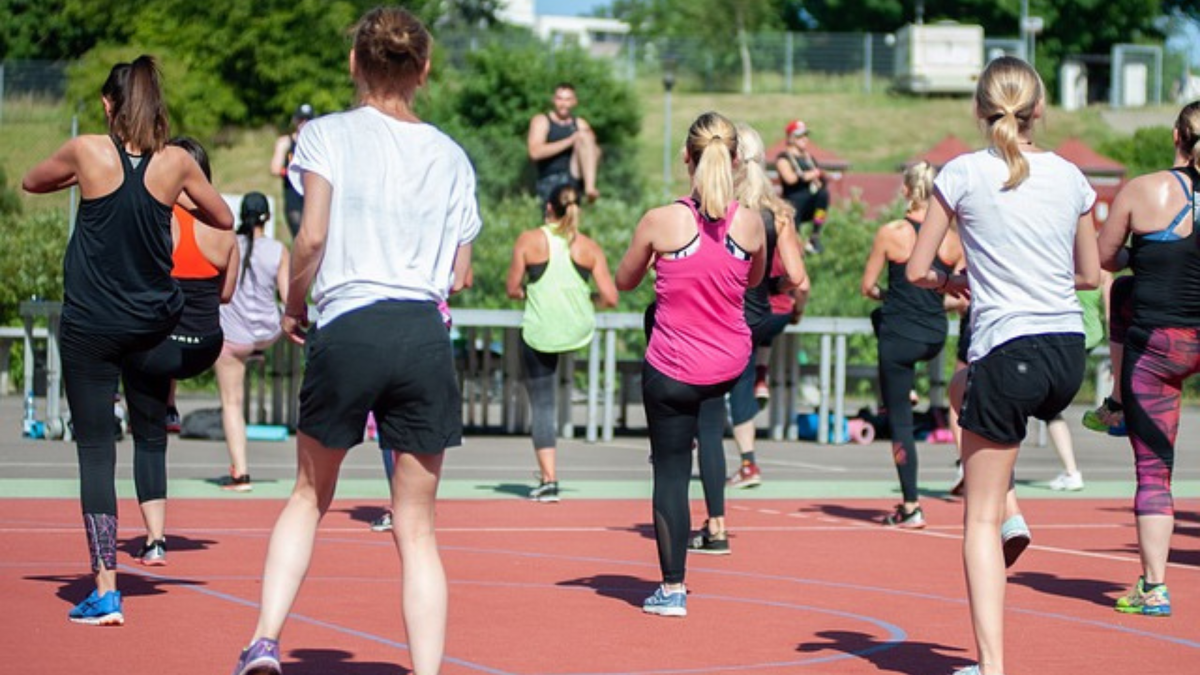A healthy lifestyle now a days typically encompasses a combination of regular exercise, balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Here are some key components:
1. Regular Exercise:
Incorporating physical activity into daily routines is crucial. This can include activities like walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or participating in sports. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by health authorities.
Regular exercise is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, offering a multitude of physical and mental health benefits. Here’s why it’s so important:
Weight Management: Exercise helps to burn calories and build muscle, making it an effective tool for weight management. It can also boost metabolism, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
Cardiovascular Health: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
Muscle Strength and Endurance: Engaging in strength training exercises helps to build and maintain muscle mass, enhancing strength and endurance. This can improve overall functional capacity and reduce the risk of injuries.
Bone Health: Weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, and resistance training help to build and maintain bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially as we age.
Mental Health: Exercise has been shown to boost mood, reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, and improve overall mental well-being. It stimulates the release of endorphins, neurotransmitters that promote feelings of happiness and relaxation.
Cognitive Function: Regular physical activity has been linked to improved cognitive function and reduced risk of cognitive decline with aging. It can enhance memory, attention, and executive function.
Improved Sleep: Exercise can help regulate sleep patterns and improve sleep quality, leading to better rest and rejuvenation.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Disease: Regular exercise has been associated with a lower risk of developing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and metabolic syndrome.
Boosted Immune Function: Moderate exercise has been shown to enhance immune function, reducing the risk of infections and illnesses.
Longevity: Studies suggest that regular physical activity is associated with a longer lifespan and reduced risk of premature mortality.
To reap these benefits, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week. Incorporate a variety of activities that you enjoy, such as walking, running, swimming, cycling, dancing, or playing sports, to keep your routine interesting and sustainable. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
2. Balanced Nutrition:
Eating a variety of nutrient-rich foods is essential for overall health. Focus on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit processed foods, added sugars, and excessive salt intake.
Balanced nutrition is essential for supporting overall health and well-being. Here are some key principles to consider when striving for a nutritious diet:
- Variety: Incorporate a wide range of foods from all food groups – fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This ensures you get a diverse array of nutrients essential for optimal health.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can lead to weight gain and other health issues. Use smaller plates, pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, and avoid eating straight from large packages.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables at each meal. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that support overall health and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread over refined grains like white rice and white bread. Whole grains provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Lean Proteins: Include a variety of lean protein sources in your diet, such as poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and low-fat dairy products. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining muscle mass.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon and tuna. These fats provide essential fatty acids that are important for brain health, hormone production, and inflammation control.
- Limit Added Sugars: Minimize consumption of foods and beverages high in added sugars, such as sugary drinks, sweets, and processed snacks. Opt for naturally sweet foods like fruits and limit added sugars to reduce the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
- Reduce Sodium Intake: Limit consumption of processed and packaged foods high in sodium, and use herbs, spices, and other flavorings to season meals instead of salt. High sodium intake is associated with high blood pressure and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Limit consumption of sugary drinks and excessive caffeine, which can contribute to dehydration and other health issues.
- Moderation and Balance: Practice moderation and balance in your eating habits. Enjoy your favorite foods occasionally, but focus on overall dietary patterns that emphasize nutrient-dense foods.
By following these principles of balanced nutrition, you can support your health, energy levels, and overall well-being. Remember that individual dietary needs may vary, so it’s essential to listen to your body and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian if you have specific.
3. Adequate Sleep:
Quality sleep is fundamental for physical and mental well-being. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, and establish a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day.
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being, impacting various aspects of physical and mental health. Here’s why it’s essential and some tips for achieving better sleep:
Importance of Adequate Sleep:
- Physical Restoration: During sleep, the body undergoes repair and restoration processes, including muscle growth, tissue repair, and immune system strengthening.
- Cognitive Function: Sleep plays a vital role in cognitive function, including memory consolidation, learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Adequate sleep enhances cognitive performance and productivity.
- Mood Regulation: Sleep influences mood and emotional regulation. Insufficient sleep can lead to irritability, mood swings, and an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
- Physical Health: Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of various health problems, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and weakened immune function.
- Hormonal Balance: Sleep affects hormone regulation, including those involved in appetite control (ghrelin and leptin), stress response (cortisol), and growth and development (growth hormone).
- Immune Function: Adequate sleep is essential for a healthy immune system. It helps the body defend against infections and illnesses by supporting immune cell function and antibody production.
- Energy Levels: Quality sleep is necessary for maintaining energy levels, alertness, and overall vitality throughout the day.
Tips for Achieving Better Sleep:
- Establish a Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s internal clock and improve sleep quality.
- Create a Restful Environment: Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it dark, quiet, and cool. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows, and consider using white noise machines or earplugs if needed.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: Avoid electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers at least an hour before bedtime, as the blue light emitted can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, practicing deep breathing exercises, or meditating, to help relax the mind and body.
- Limit Caffeine and Stimulants: Avoid consuming caffeine and other stimulants in the afternoon and evening, as they can disrupt sleep patterns and make it harder to fall asleep.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can promote better sleep, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it may energize you and make it difficult to wind down.
- Watch Your Diet: Avoid heavy meals, spicy foods, and excessive fluid intake close to bedtime, as they can cause discomfort and disrupt sleep.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation before bed.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you continue to experience persistent sleep problems despite trying these strategies, consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist for further evaluation and treatment options.
By prioritizing sleep and adopting healthy sleep habits, you can improve your overall health, mood, and quality of life.
4. Stress:
Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on health. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
Stress management is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being, as chronic stress can have detrimental effects on both physical and mental health. Here are some strategies for effectively managing stress:
- Identify Stressors: Recognize the sources of stress in your life, whether they’re related to work, relationships, finances, health concerns, or other factors. Understanding what triggers stress can help you develop targeted strategies for coping.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, yoga, or tai chi. These practices can help calm the mind, reduce muscle tension, and promote a sense of relaxation and well-being.
- Engage in Physical Activity: Regular exercise is a powerful stress reliever, as it helps release endorphins, neurotransmitters that improve mood and reduce stress. Find activities you enjoy, whether it’s walking, jogging, cycling, dancing, or participating in sports, and aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Set Boundaries: Learn to say no to additional commitments or responsibilities when you’re feeling overwhelmed. Establishing boundaries around your time and energy can help prevent burnout and reduce stress levels.
- Practice Time Management: Prioritize tasks and break them down into manageable steps to avoid feeling overwhelmed. Use tools such as to-do lists, calendars, and time-blocking techniques to organize your schedule and allocate time for important activities, including relaxation and self-care.
- Cultivate Healthy Habits: Maintain a balanced diet, get adequate sleep, and avoid excessive caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco, as these substances can exacerbate stress. Nourishing your body with nutritious food and sufficient rest can enhance your resilience to stress.
- Seek Social Support: Reach out to friends, family members, or support groups for emotional support and encouragement during stressful times. Talking to someone you trust can provide perspective, validation, and reassurance.
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment, which can help reduce stress and enhance overall well-being. Engage in mindfulness practices such as mindful breathing, mindful eating, or body scan meditation to cultivate awareness and acceptance of your thoughts and feelings.
- Engage in Hobbies and Leisure Activities: Make time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation, whether it’s reading, gardening, painting, listening to music, or spending time in nature. Engaging in hobbies and leisure pursuits can provide a much-needed break from stressors and promote a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you’re struggling to manage stress on your own or experiencing persistent symptoms of anxiety or depression, don’t hesitate to seek support from a mental health professional. Therapy, counseling, or stress management programs can provide tools and strategies to help you cope more effectively with stress.
By incorporating these stress management techniques into your daily life, you can build resilience, reduce the impact of stressors, and improve your overall quality of life.
5. Hydration:
Staying hydrated is vital for various bodily functions. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, and limit consumption of sugary beverages and excessive caffeine.
Hydration is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being, as water plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions. Here’s why hydration is important and some tips for ensuring adequate fluid intake:
Importance of Hydration:
- Regulation of Body Temperature: Water helps regulate body temperature through sweating and evaporation, particularly during physical activity or in hot environments.
- Transportation of Nutrients: Water is essential for transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells throughout the body, facilitating the proper functioning of organs and tissues.
- Removal of Waste Products: Adequate hydration supports the elimination of waste products and toxins from the body through urine and sweat, helping maintain kidney function and overall detoxification.
- Joint Lubrication: Water lubricates and cushions joints, reducing friction and preventing discomfort or injury during movement.
- Digestive Health: Water aids in digestion by softening stools and promoting regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of constipation and digestive problems.
- Cognitive Function: Dehydration can impair cognitive function, leading to decreased concentration, alertness, and mental clarity. Staying hydrated is essential for optimal brain function and performance.
- Skin Health: Proper hydration contributes to healthy, glowing skin by maintaining moisture levels and supporting skin elasticity. Dehydration can lead to dryness, flakiness, and premature aging of the skin.
Tips for Hydration:
- Drink Plenty of Water: The most straightforward way to stay hydrated is to drink water throughout the day. Aim for at least 8-10 cups (about 2-2.5 liters) of water per day, or more if you’re physically active or in a hot climate.
- Monitor Urine Color: Check the color of your urine as a simple indicator of hydration status. Pale yellow or straw-colored urine generally indicates adequate hydration, while darker urine may indicate dehydration and the need to drink more fluids.
- Incorporate Hydrating Foods: Many fruits and vegetables have high water content and can contribute to hydration. Include hydrating foods such as watermelon, cucumbers, oranges, strawberries, celery, and tomatoes in your diet.
- Sip Water Throughout the Day: Instead of waiting until you’re thirsty, make it a habit to sip water regularly throughout the day to maintain hydration levels. Keep a reusable water bottle with you and take frequent breaks to hydrate, especially during periods of physical activity or in warm environments.
- Hydrate Before, During, and After Exercise: Drink water before, during, and after exercise to replenish fluids lost through sweating and prevent dehydration. Sports drinks may be beneficial for prolonged or intense exercise sessions to replace electrolytes lost through sweat.
- Limit Dehydrating Beverages: Minimize consumption of beverages that can contribute to dehydration, such as caffeinated drinks (coffee, tea, soda) and alcoholic beverages. These drinks have diuretic effects and can increase fluid loss.
- Pay Attention to Thirst: Thirst is a natural signal from your body indicating the need for fluids. Don’t ignore thirst cues and respond promptly by drinking water or other hydrating beverages.
- Adjust Fluid Intake Based on Individual Needs: Factors such as age, weight, activity level, climate, and overall health can influence fluid requirements. Listen to your body and adjust your fluid intake accordingly to maintain optimal hydration.
By prioritizing hydration and incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can support your overall health, energy levels, and well-being. Remember that staying adequately hydrated is essential for optimal physical and mental function.
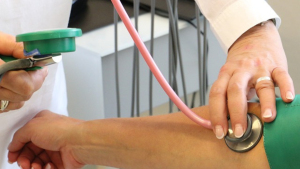
6. Regular Health Check-ups:
Schedule regular visits with healthcare professionals for preventive screenings and assessments. This can help detect any potential health issues early on and facilitate timely interventions.
Regular health check-ups are an essential aspect of preventive healthcare, allowing individuals to monitor their health status, detect potential health issues early, and take proactive steps to maintain or improve their well-being. Here’s why regular check-ups are important and what they typically entail:
Importance of Regular Health Check-ups:
- Early Detection of Health Issues: Regular check-ups enable healthcare professionals to screen for various health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, certain cancers, and other chronic diseases. Detecting these conditions early increases the likelihood of successful treatment and better health outcomes.
- Preventive Care: Health check-ups often include preventive interventions such as vaccinations, screenings, and lifestyle counseling to reduce the risk of developing certain diseases and promote overall health and well-being.
- Monitoring Chronic Conditions: For individuals with chronic health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, asthma, or heart disease, regular check-ups are essential for monitoring disease progression, adjusting treatment plans, and preventing complications.
- Risk Assessment and Health Education: Healthcare providers can assess an individual’s risk factors for various health conditions based on factors such as family history, lifestyle habits, and medical history. They can also provide personalized health education and guidance on preventive measures to optimize health and reduce risks.
- Establishing a Relationship with a Healthcare Provider: Regular check-ups allow individuals to establish a trusting relationship with a primary care provider or healthcare team. This relationship fosters open communication, continuity of care, and personalized health management.
Typical Components of Regular Health Check-ups:
- Medical History Review: Healthcare providers typically begin by reviewing the individual’s medical history, including past illnesses, surgeries, medications, allergies, and family medical history.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is conducted to assess vital signs (such as blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature), overall health status, and any signs of illness or abnormalities.
- Laboratory Tests and Screenings: Depending on age, gender, and individual risk factors, health check-ups may include various laboratory tests and screenings, such as blood tests (e.g., cholesterol, glucose), urine analysis, cancer screenings (e.g., mammograms, Pap smears, colonoscopies), and immunizations.
- Lifestyle Assessment and Counseling: Healthcare providers often discuss lifestyle factors that impact health, such as diet, physical activity, smoking, alcohol consumption, stress management, and sleep habits. They may provide guidance and support to help individuals make healthy lifestyle changes.
- Discussion of Health Concerns and Goals: Health check-ups provide an opportunity for individuals to discuss any health concerns, symptoms, or questions they may have with their healthcare provider. Providers can offer advice, address concerns, and collaborate with individuals to set health goals and develop personalized care plans.
- Follow-up and Referrals: Based on the findings of the check-up, healthcare providers may recommend follow-up appointments, additional tests, referrals to specialists, or adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
By scheduling regular health check-ups and actively participating in preventive healthcare, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their health, detect health issues early, and optimize their overall well-being. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate frequency and components of check-ups based on individual health needs and risk factors.
Healthy Lifestyle
Related posts
 Healthy LifestyleIn Healthy Lifestyle
Healthy LifestyleIn Healthy Lifestyle Healthy Diet Food PlanIn Diet Plans
Healthy Diet Food PlanIn Diet Plans Planning a Healthy DietIn Healthy Lifestyle
Planning a Healthy DietIn Healthy Lifestyle Vegetable LasagneIn Recipes
Vegetable LasagneIn Recipes